Faulty Shock Absorber: Signs and Impact
Shock absorber faults significantly affect a car's behaviour on the road. Specifically, the vehicle's nose "dives" during braking and "squats" during acceleration, stopping distances increase, body roll becomes excessive during manoeuvring, and the car sways when driving over uneven surfaces.
There are both obvious and hidden signs of faulty shock absorbers. Obvious signs include oil leaks (wear of the oil seal and/or piston rod), but there are more hidden indicators, such as fluid degradation, deformation of the valve mechanism plates, and wear of the piston seal and internal walls of the working cylinder. To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is essential to identify shock absorber faults in good time.

Signs of Faulty Shock Absorbers
There are two types of signs indicating that a shock absorber has partially or completely failed. The first type is visual, which can be identified during a physical inspection of the unit. The second type relates to changes in the vehicle's behaviour while driving. We will list the behavioural signs first, as you should primarily pay attention to how the car handles on the road:
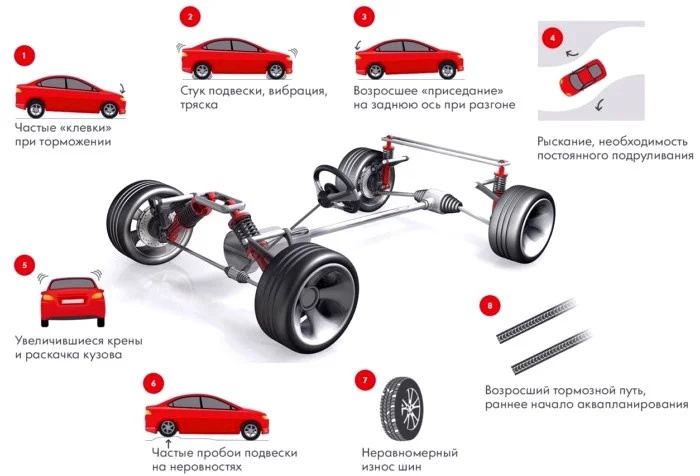
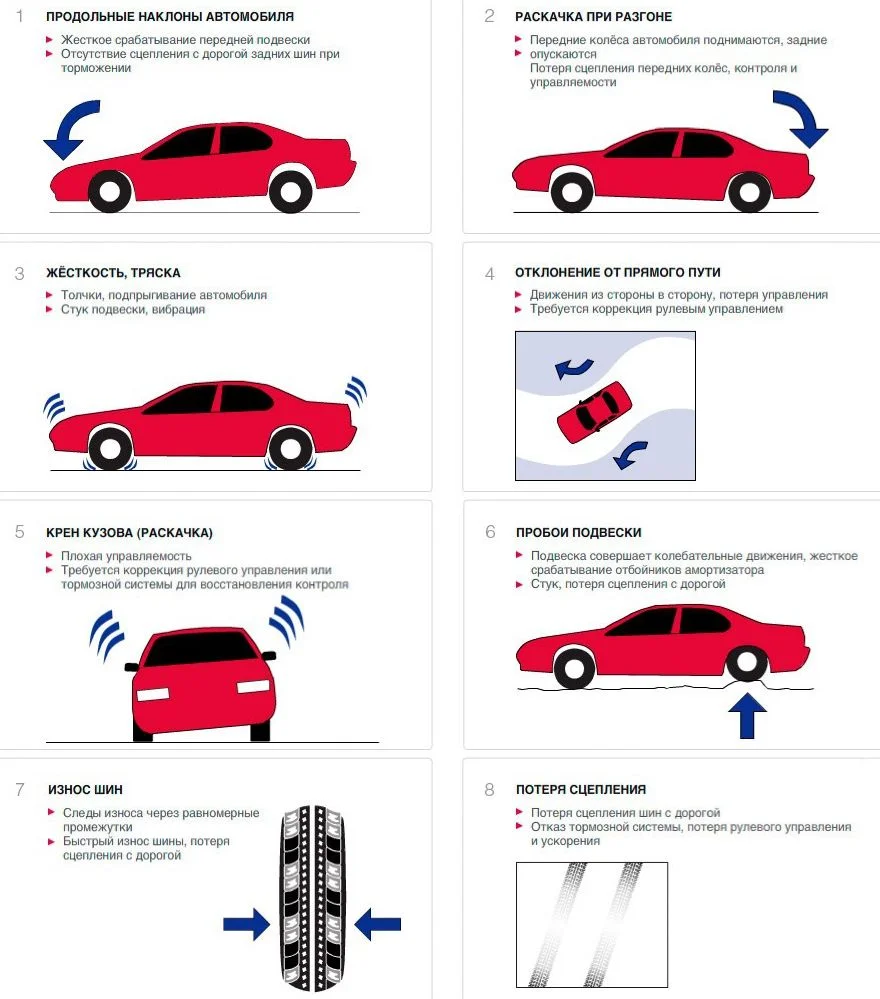
- Swaying during braking and acceleration. If the shock absorbers are in good condition, the car should not bounce back more than once even after sharp braking; the damper should absorb the oscillation immediately. If there are two or more bounces, this is a symptom of partial or total failure.
- Body roll when manoeuvring. The situation is similar here: after exiting a sharp turn, the bodywork should not continue to rock sideways. If it does, the shock absorber is likely faulty.
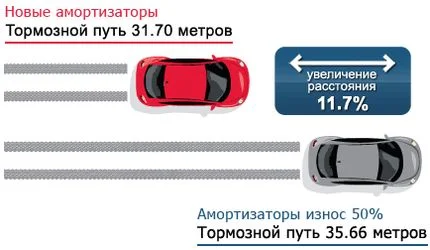
- Increased braking distance. This factor is caused by the same swaying effect during braking. As the shock absorber fails to dampen vibrations during sustained braking, the front of the car periodically dips and rises. This reduces the load on the front wheels, thereby decreasing braking efficiency. Stopping distances increase significantly on cars equipped with ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), as the rear wheels lift, prompting the ABS to reduce pressure in the brake lines. Braking distance also increases on uneven roads.
- The car "wanders" on the road. Even with the steering wheel held straight, the vehicle constantly pulls to the side, requiring the driver to make constant steering corrections to maintain a straight line.
- Driving discomfort. This can manifest in various ways. Constant swaying can cause discomfort for drivers and passengers on long journeys, leading to motion sickness (kinetosis). This effect is a typical symptom of faulty rear shock absorbers.
Note that signs such as increased braking distance, uneven tyre wear, and the constant need for steering corrections can indicate other vehicle issues, such as worn brake pads, low brake fluid, uneven tyre pressure, problems with ball joints, or other suspension components. Therefore, a comprehensive diagnostic is recommended. Visual symptoms of shock absorber wear include:
- Appearance of leaks on the housing and piston rod. This usually occurs due to wear of the oil seal and/or the shock absorber rod. A drop in oil level reduces the unit's working amplitude and increases wear on internal parts.
- Wear of silent blocks (bushes). As known, mobility in this rubber-metal joint is provided by the elasticity of the rubber (or polyurethane). If the shock absorber works too rigidly, excessive force is transferred to the silent block, leading to significant wear and failure. Therefore, when diagnosing shocks, it always makes sense to check the condition of the silent blocks as well.
- Damage to the shock absorber housing and/or its mountings. This can manifest as rust on the piston rod (strut, mount), housing distortion, damaged mounting bolts, etc. In any case, the unit must be inspected carefully.
- Uneven tyre wear. Typically, tyres wear more on the inside and less on the outside.
In summary, if a shock absorber fault arises, expect other suspension elements to fail soon, as they are all interconnected and influence one another.
Impact of Shock Absorber Failure
Driving with worn shock absorbers is not only uncomfortable but can be genuinely dangerous. Possible problems associated with faulty dampers include:
- Reduced wheel grip on the road. Specifically, as the car sways, the grip levels fluctuate constantly.
- Increased braking distance, especially on vehicles with ABS.
- Potential malfunction of electronic systems such as ABS and ESP (Electronic Stability Programme).
- Deterioration of vehicle handling, particularly at high speeds.
- Occurrence of "aquaplaning" on wet roads even at lower speeds.
- During night driving, constant pitching of the front end can cause headlights to dazzle oncoming drivers.
- Driving discomfort, which leads to increased driver fatigue on long journeys and risk of motion sickness for passengers.
- Accelerated wear of tyres, rubber bushes, silent blocks, bump stops, springs, and other suspension components.
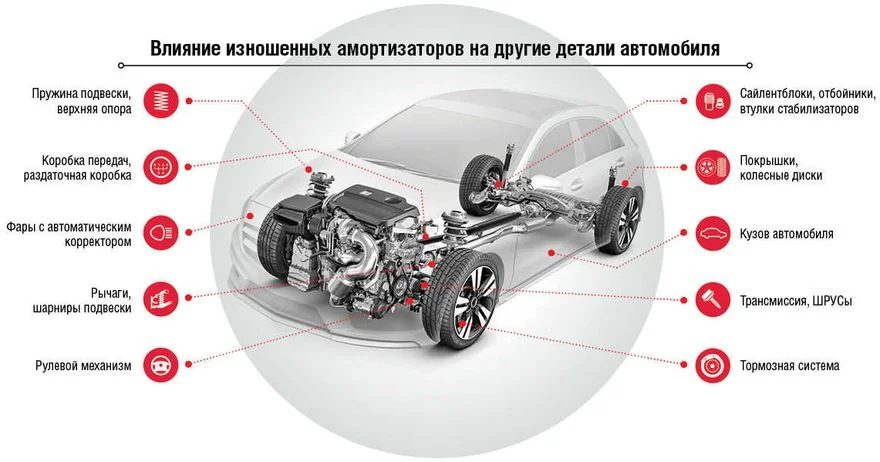
Causes of Shock Absorber Failure
The causes of failure are generally natural factors, including:

- Degradation of the damping fluid (oil). Like other technical fluids in a car, the oil in the shock absorber gradually absorbs moisture and loses its performance properties. This naturally causes the shock to work more rigidly than before. However, fluid aging does not happen overnight, unless the housing seal ruptures.
- Torn oil seal. Specifically, the seal for the piston and the inner walls of the working cylinder. The seal can tear due to external factors or simply due to aging. Like any rubber seal, it hardens over time and begins to leak. This leads to oil leaking out and moisture getting in, degrading the fluid's characteristics.
- Deformation of valve mechanism plates. This is also a natural process that occurs continuously, albeit at different rates. The rate of deformation depends on two main factors: the quality of the shock absorber (metal quality of the plates) and the operating conditions (significant impact loads lead to premature deformation).
- Gas leakage. This applies to gas-filled shock absorbers. The principle is the same as for oil-filled units. The gas performs a damping function; if it's gone, the shock won't work.
- Failure of silent blocks. They wear out for natural reasons, losing elasticity and functionality. These components are practically unrepairable, so they must simply be replaced (if possible, otherwise the entire shock absorber must be changed).
How to Identify Shock Absorber Faults
Car owners are rightly concerned about how to check oil or gas-oil shock absorbers. Modern damping units often have a more complex design than older models, complicating diagnostic measures. Ideally, they should be checked at a service centre on a special test stand. However, there are several "DIY" methods for checking them.
The Bounce Test
The simplest, "traditional" method involves rocking the car body. You push down hard on the front or rear corners, or individual shock absorbers. You need to push firmly, but be careful not to dent the bodywork (this actually happens in practice!). In theory, you need to achieve the maximum possible amplitude of swaying, then release the body and watch its subsequent oscillations.

If the shock absorber is healthy, the body will make one bounce (or one and a half), then settle and remain in the initial position. If the shock is faulty, the body will continue to oscillate two or more times. In this case, replacement is required.
It is worth noting that the bounce method is suitable for cars with simple suspension systems, such as classic older saloons. Modern cars often use complex (often multi-link) suspension, which will dampen oscillations even with faulty shock absorbers. Therefore, the bounce test essentially identifies two extreme states: the damper has completely failed, or it is seizing up. It is difficult to detect "intermediate" wear states using this method.
Visual Inspection
When diagnosing a problematic shock absorber, a visual inspection is mandatory. To do this, drive the car over an inspection pit or raise it on a lift. You can, of course, remove the shock absorber, but that takes a lot of time and effort. During the inspection, check for oil leaks on the housing. You can wipe off oil traces with a rag and leave it for a few days. After this period, repeat the check.

If the car is on a lift, check the condition of the piston rods. There should be no signs of rust or damage. If present, the unit is at least partially faulty and requires further diagnostics.
During the inspection, pay attention to the nature of tyre wear. Often, with broken shock absorbers, tyres wear unevenly; typically, the main wear is on the inner part of the tyre. There may also be isolated "bald spots" on the rubber (cupping). However, tread wear can indicate other suspension faults, so additional diagnostics are needed here too.
If checking front struts, inspecting the springs and top mounts is mandatory. Suspension springs must be intact, without cracks or mechanical damage.
Road Test Inspection
If one or more shock absorbers are faulty, the driver will feel the car "wandering" on the road, requiring constant steering corrections to keep it in the lane. The car will pitch during acceleration and braking. The same applies to body roll. You don't necessarily need to drive at high speeds; city speeds are sufficient for testing. Specifically, at 30–40 mph (50–60 km/h), you can perform sharp acceleration, braking, and gentle slalom manoeuvres.
When to Replace Shock Absorbers
It is important to understand that regardless of the shock absorber's quality or the car's operating conditions, wear on this component is constant. It happens faster or slower, but it is continuous! Consequently, their condition must be checked regularly. Most manufacturers of mid-range shock absorbers recommend performing a check every 12,000–18,000 miles (20–30,000 km). As for replacement, a shock absorber typically shows significant wear after approximately 50,000–60,000 miles (80–100,000 km). At this stage, a more thorough check and, if necessary, replacement should be performed.
To make your shock absorbers last as long as possible, follow these recommendations:
- Do not overload the car. The manual for any vehicle clearly states its maximum load capacity. Do not exceed this, as it is harmful to various components — including the engine and suspension elements, specifically the shock absorbers.
- Allow them to warm up. When driving in cold weather (especially in freezing temperatures), try to drive the first half-mile (500–1,000 metres) at a low speed and avoid bumps. This allows the oil to warm up and flow properly.
Thus, if problems with shock absorbers appear, it is better not to delay and replace the faulty units with new ones. Regarding purchasing, it is best to buy licensed parts from authorised dealers or choose products from proven shops based on reviews from other motorists.
Was this article useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.







Discussion (0)
No comments yet!