Error P0016: Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Correlation — Causes and Fixes
Error code P0016 informs the driver that the ECU (Electronic Control Unit) has detected a loss of synchronisation between the position of the crankshaft and the camshaft. The code appears when the signals from the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors (CKP and CMP) fall outside the permissible range relative to each other.
Why does code P0016 appear?
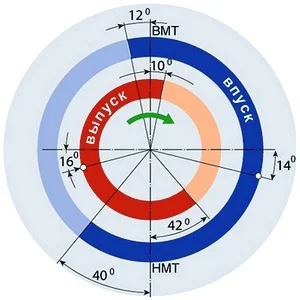
Valve timing — moments of valve opening and closing, expressed in degrees of crankshaft rotation.
The ECU uses shaft position data to determine the compression stroke in the cylinders and the precise moment for fuel injection. If the control unit does not receive correct synchronisation information, it generates a fault code. In this scenario, the engine often enters a 'limp mode' (e.g., using batch injection) to keep the vehicle drivable.
This error is predominantly characteristic of vehicles with a timing chain (due to chain stretch), but it also occurs on engines with a timing belt. Vehicle behaviour can vary: from unnoticeable to the driver, to a tangible loss of power and unstable engine operation (misfiring). The error can manifest in various modes: during startup, at idle, or under load.
Conditions for fault registration
The error code is recorded in the ECU memory when the pulse from the camshaft sensor does not match the expected signal interval from the crankshaft. The 'Check Engine' light usually illuminates after the fault has been registered over several engine operating cycles. If the problem is intermittent (comes and goes), it often points to poor contact in connectors, damaged wiring insulation, or oil pressure issues within the variable valve timing system.
Causes of the error
To diagnose error P0016, five main components should be checked:
- Electrical wiring and sensor contacts (oxidation, breaks).
- Engine oil condition (low level, contamination) and oil channels.
- The position sensors themselves (CKP and CMP) and their reluctor rings.
- The OCV valve (Oil Control Valve).
- The Variable Valve Timing unit (phaser/VVT gear).
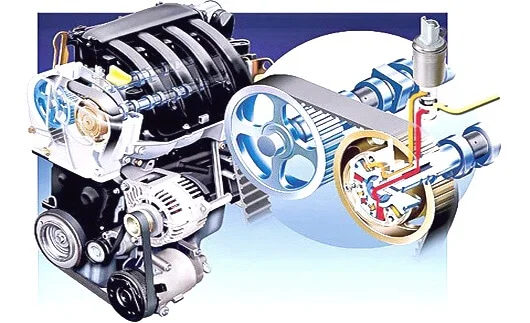
VVT-i System
In most cases on modern engines, the shaft mismatch error is linked to issues with the VVT system or the timing mechanism:
- Timing chain stretch (misalignment of timing marks).
- Wear or failure of the hydraulic tensioner and chain guides.
- Seizing or wear of the VVT hub.
- Contamination of the VVT valve mesh filter.
Diagnostic and repair methods
Fault finding should start from the simple to the complex:
- Visual inspection. Check the connectors and wiring of the CKP and CMP sensors for breaks, corrosion, or oil contamination.
- Sensor check. Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to check the signal from the sensors. Also, inspect the reluctor rings (marker rings) on the shafts — bent teeth or magnetised swarf can distort the signal.
- VVT System. Check the oil level and cleanliness. Remove and clean the OCV valve; apply voltage (usually 12V) to it to ensure the plunger moves freely.
- Timing marks. If the previous steps did not help, you must remove the timing cover and check the alignment of the crankshaft and camshaft marks, as well as the extension of the tensioner (to assess chain stretch).
Ignoring the problem (especially regarding chain stretch) can lead to the chain jumping teeth, pistons striking the valves, and the need for a major engine overhaul.
If the error appeared immediately after engine repairs, there is a high probability that the cause is incorrect timing mark alignment or loose fasteners on the pulleys/gears.
Was this article useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials






Discussion (0)
No comments yet!