Car Battery Charging Time Calculator
It is not only a completely flat battery (a situation best avoided) that requires charging, but also a battery currently in use. However, the charging time for each will be different. Often, this ranges from 8 to 12 hours. Our online calculator will help you calculate exactly how long you need to charge your car battery using a constant current method.
When, how, and at what current to charge
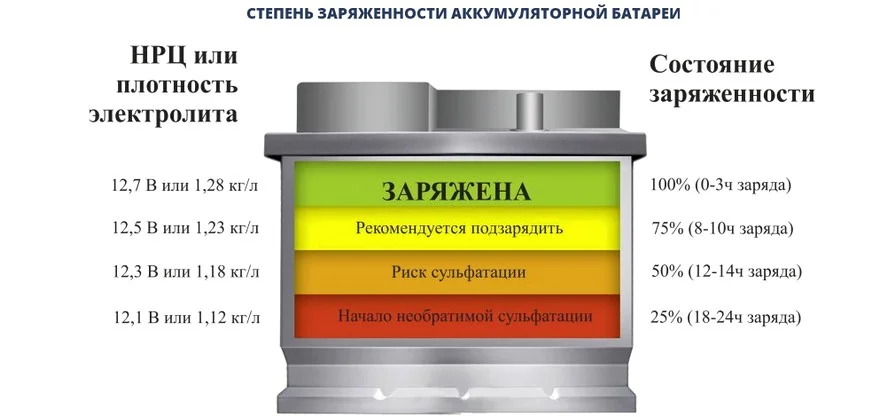
Typically, the state of charge (SoC) of a battery is judged by the specific gravity (density) of its electrolyte. The density of a fully charged battery should be 1.26–1.28 g/cm³, and the voltage should be no less than 12.5 V (it may be 12.7–12.9 V depending on the climate and initial specification). The lower the density, the more discharged the battery is. A decrease in density of 0.01 g/cm³ compared to the nominal value indicates that the battery has discharged by approximately 6–8%. The state of charge should be determined by the cell with the lowest density.
| State of Charge (%) | Electrolyte Density (g/cm³) | Depth of Discharge (%) | Battery Voltage (V) | Charging Time at 10% Capacity (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1.277 | 0 | 12.73 | Not necessary |
| 90 | 1.258 | 10 | 12.62 | 2 |
| 80 | 1.238 | 20 | 12.50 | 4 |
| 70 | 1.217 | 30 | 12.37 | 6 |
| 60 | 1.195 | 40 | 12.24 | 8 |
| 50 | 1.172 | 50 | 12.10 | 10 |
| 40 | 1.148 | 60 | 11.96 | 13 |
| 30 | 1.124 | 70 | 11.81 | 16 |
| 20 | 1.098 | 80 | 11.66 | 20 |
| 10 | 1.073 | 90 | 11.51 | 24 |
| 0 | 1.06 | 100 | 11.4 | Sulphation |
A lead-acid battery discharged by more than 50% in summer, or even just over 25% in winter, must be removed and recharged. Additionally, any battery where the density between cells differs by more than 0.02 g/cm³ requires supplementary charging.
The optimal charging current is considered to be a current equal to 0.05 of the battery's capacity (equalising charge). For example, for a 55 Ah battery, this value is 2.75 A, and for a 60 Ah battery, it is 3 Amps. The goal of this method is to ensure the full restoration of active mass in all battery plates.
More commonly, a standard charge using a current of 10% of the capacity (0.1C) is used. That is, a 55 Ah battery is charged with 5.5 A, and a 60 Ah battery with 6 A. It is worth noting that the lower the charging current, the deeper and higher quality the charge, although it requires more time.
Battery charging methods:
- Constant current;
- Constant voltage;
- Combined (automatic mode).
Stages of car battery discharge
Battery charging time with constant current
Charging time calculation formula: T = Q / I, where Q is the capacity to be replenished (Ah), and I is the charging current (A).
To estimate the charging time with constant current, first determine the depth of discharge (in %), calculate the lost capacity (in Ah), select the current (usually 10% of the nominal capacity), and calculate the time. A margin of time must be added to the result, as the process efficiency is not 100%.
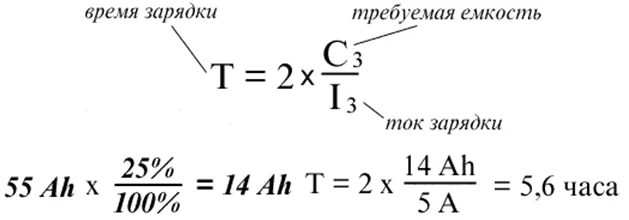
Typically, about 10–20% (a coefficient of 1.1–1.2) is added to the calculated time, as part of the energy is lost to heat and electrochemical processes. Do not double the time—this will lead to overcharging and electrolyte boiling off (gassing).
When the voltage at the terminals stops rising for an hour or two during charging, and the electrolyte is actively "gassing" (bubbling), the battery is fully charged.
How to use the calculator
To find out how long you need to charge your battery without getting bogged down in formulas, simply use this calculator.
Fill in the fields for the online calculation:
- "Nominal Capacity" — the capacity of your car battery (Ah).
- "Depth of Discharge" — the percentage calculated from the density table, or voltage measured with a voltmeter (off-load, after resting).
- "Charging Current" — the amperage you will set on the charger (usually 10% of the capacity).
Click "Calculate" to get the estimated time until full charge.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How long should I charge the battery to start the car?
To start the car in summer, it is often enough to charge the battery for 30 minutes at a current of 10% of capacity. This is sufficient to raise the voltage so the starter motor can engage. In winter, it is better to charge the battery for at least 1 hour. Further charging will occur from the alternator while driving.
-
What determines the battery charging speed?
Charging speed depends on the current strength (Amps). The higher the current, the faster the process, but the battery will heat up more. Exceeding the recommended current values (1/10 of capacity) to speed up the process is harmful to the plates.
-
How many Amps should I set when charging?
The nominal charging current is 10% of the battery capacity. For example, for a 60 Ah battery, you should set it to 6 Amps. For a gentler charge, you can set it lower (e.g., 2–3 A); the charging time will increase, but the charge will be deeper and denser.
-
How long does it take to charge a 60 Ah battery?
It depends on the depth of discharge. A completely flat 60 Ah battery charged at 6 A will take about 10–12 hours (accounting for current drop at the end of the process with automatic chargers). If the battery is only half discharged, 5–7 hours will suffice.
-
How many Amps should a fully charged battery show?
This question is slightly misunderstood. Charge level is checked by voltage (Volts) or density, not by Amps on the battery itself. However, if looking at the charger's ammeter: when charging with constant voltage, the current drops to almost zero (0.1–0.5 A) by the end of the process. When charging with constant current, the ammeter needle will stay where you set it, but the voltage will rise to 14.4 V (or higher for Calcium batteries), and gassing will begin.
Was this tool useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials




Discussion (0)
No comments yet!