Car Engine Power Calculator
Let's look at 5 popular ways to calculate car engine power using data such as:
- engine RPM,
- engine displacement,
- torque,
- mean effective pressure in the combustion chamber,
- fuel consumption,
- injector flow rate,
- vehicle weight,
- 0–100 km/h acceleration time.
Each formula used for the engine power calculation is relatively approximate and cannot determine the real horsepower driving the car with 100% accuracy. However, by calculating with each of these approximation methods and relying on specific indicators, you can calculate an average value (whether for a stock or tuned engine) with a margin of error of about 10%.
Power is the energy produced by the engine, which is converted into torque at the output shaft of the internal combustion engine (ICE). This is not a constant value. Maximum power figures are always quoted alongside the RPM at which they are achieved. The peak is reached at the highest mean effective pressure in the cylinder (depending on the quality of the fresh fuel mixture intake, combustion completeness, and thermal losses). Modern engines deliver maximum power on average at 5500–6500 rpm. In the automotive sector, it is standard to measure engine power in horsepower. Since most formulas output the result in kilowatts, you may need a calculator to convert kW to hp.
How to calculate power using torque
The simplest car engine power calculation can be determined by the relationship between torque and RPM.
Torque
Force multiplied by the leverage of its application, which the engine can deliver to overcome resistance to movement. It determines how quickly the engine reaches maximum power. The formula for calculating torque from engine displacement is:
M = VH x PE / 0.12566, where
- VH – engine displacement (litres),
- PE – mean effective pressure in the combustion chamber (bar).
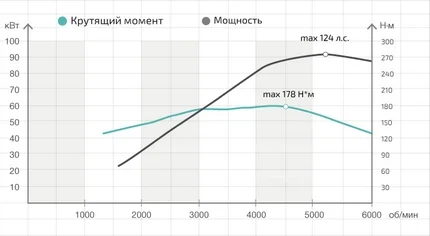
Engine RPM
The rotational speed of the crankshaft.
The formula for calculating the power of an internal combustion engine is as follows:
P = M * n / 9549 [kW], where:
- M – engine torque (Nm),
- n – crankshaft speed (rpm),
- 9549 – a coefficient for unit alignment (allows inputting rpm and receiving the result in kW).
Since the formula yields a result in kW, it can be converted to horsepower if necessary by multiplying by a factor of 1.36.
Using these formulas is the simplest way to translate torque into power.
To avoid getting bogged down in details, you can perform a quick online ICE power calculation using our calculator.
How to calculate power by engine displacement
If you do not know the torque of your car's engine, you can also use the following formula to determine its power in kilowatts:
Ne = Vh * pe * n / 120 (kW), where:
- Vh — engine displacement, cm³
- n — rotational speed, rpm
- pe — mean effective pressure, MPa (on standard petrol engines this is around 0.82 – 0.85 MPa, tuned engines – 0.9 MPa, and for diesel from 0.9 up to 2.5 MPa respectively).
To get the engine power in "horses" rather than kilowatts, divide the result by 0.735.
Engine power calculation by air flow
A similarly approximate engine power calculation can be determined by air consumption. This function is available to those with an on-board computer or diagnostic scanner installed, as it is necessary to record the flow rate value when the car engine (usually in third gear) is spun up to 5,500 rpm.
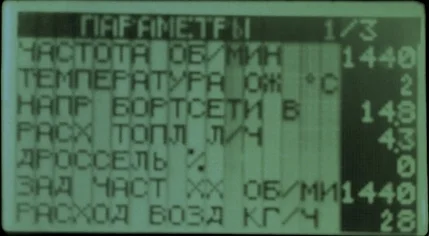
The formula for calculating ICE power by air flow looks like this:
Air mass [kg/h] / 3 = P [hp]
This calculation, like the previous one, shows gross power (excluding losses), which is 10—20% higher than the actual wheel horsepower. It is also worth noting that MAF sensor readings depend heavily on its cleanliness and calibration.
Power calculation by weight and acceleration time

Another interesting way to calculate engine power on any type of fuel is by acceleration dynamics. This uses the vehicle mass (including the driver) and the time to accelerate to 100 km/h. To make the calculation as close to the truth as possible, one must also account for traction loss depending on the drive type and gear shifting speed. Approximate start losses for front-wheel drive are 0.5 sec, and 0.3-0.4 sec for rear-wheel drive cars.
Using this ICE power calculator, which helps determine engine power based on acceleration dynamics and mass, you can quickly find out your vehicle's parameters without delving into complex physics formulas.
ICE power calculation by injector flow rate
An equally effective indicator of car engine power is injector performance. We have previously discussed its calculation and relationship, so calculating the number of horsepower using the formula will not be difficult. The estimated power calculation follows this scheme:
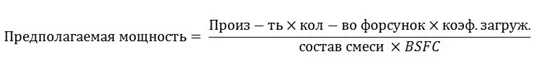
Where the duty cycle coefficient is no more than 75-80% (0.75...0.8), the mixture composition at maximum performance is around 12.5 (rich), and the BSFC coefficient will depend on the engine type (naturally aspirated — 0.4-0.52, turbocharged — 0.6-0.75).
Having found all the necessary data, enter the figures into the corresponding cells of the calculator. By clicking the "Calculate" button, you will receive a result showing the real power of your car's engine with a small margin of error. Note that you do not necessarily need to know all the presented parameters; you can calculate ICE power using a single chosen method.
The value of this calculator lies not so much in calculating the power of a stock car, but in evaluating changes if your vehicle has undergone tuning.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How to calculate internal combustion engine power?
Engine power in kW can be calculated using engine displacement and crankshaft RPM. The engine power calculation formula is:
Ne = Vh * Pe * n / 120 (kW), where:
Vh — engine displacement, cm³
n — number of crankshaft revolutions per minute
Pe — mean effective pressure, MPa -
Which coefficient should be used when calculating engine power?
For an ICE, efficiency and transmission losses are important. If converting kW to hp, a coefficient of 1.36 is used. The sometimes mentioned power factor (cosφ) applies only to electric motors and is not used for ICE power calculations.
-
How to calculate engine power by torque?
To determine engine power in kilowatts when torque is known, the formula is: P = M * n / 9549, where:
M – torque (Nm),
n – crankshaft speed (rpm),
9549 – coefficient for converting revolutions to radians and aligning units of measurement. -
How to calculate engine power by air flow?
You can calculate approximate engine power in hp, knowing its air consumption (if an on-board computer is present), using an empirical formula. It is necessary to record the mass air flow (kg/h) at maximum power RPM (usually around 5500 rpm) and divide this value by 3.
Was this tool useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials






Discussion (0)
No comments yet!