Internal Combustion Engine Displacement Calculator
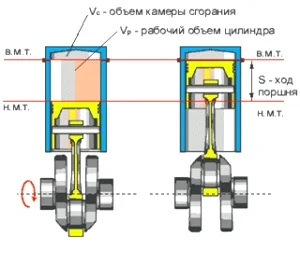
The working volume (displacement) of a cylinder represents the volume found between the extreme positions of the piston's movement.
The formula for calculating cylinder volume is well known from school geometry – volume equals the area of the base multiplied by the height. To calculate the engine displacement of a car or motorcycle, we use the same factors. The working volume of any engine cylinder is calculated as follows:
Where:
h — piston stroke length in mm within the cylinder from TDC to BDC (Top Dead Centre and Bottom Dead Centre)
r — piston radius in mm
π — 3.14 (mathematical constant)
Alternatively, using the formula: V=(πD²/4)h, where D (cylinder diameter/bore) is used instead of the radius. For example, to calculate the displacement of a typical 2.7-litre SUV engine, we take the following data:
- Cylinder diameter (Bore): 95.5 mm (Radius — 47.75 mm).
- Piston stroke: 94 mm.
- Number of cylinders: 4.
Entering these figures into the calculator gives a volume of 2693 cc (cubic centimetres).
For comparison, let's calculate the volume of a standard 1.6-litre hatchback engine. According to the specifications:
- Cylinder diameter (Bore): 82 mm (Radius = 41 mm).
- Piston stroke: 75.6 mm.
- Number of cylinders: 4.
The calculator gives a volume of 1596 cc. According to technical specifications, this result matches the factory data exactly.
How to find out engine displacement
To calculate the total engine displacement, you need to calculate the volume of a single cylinder and then multiply it by the number of cylinders in the ICE (Internal Combustion Engine). Thus:
V_engine = Pi multiplied by the radius squared (piston bore) multiplied by the stroke height and multiplied by the number of cylinders.
Since piston parameters are usually specified in millimetres, while engine displacement is measured in cubic centimetres (cc), the result must be divided by 1000 to convert the units.
Note that the total volume and working volume (swept volume) differ. The piston has crowns and valve recesses, and the total volume also includes the volume of the combustion chamber. Therefore, do not confuse these two concepts. To calculate the real (total) volume of a cylinder, you must sum the combustion chamber volume and the working volume.
You can determine engine displacement with a standard calculator if you know the cylinder and piston parameters. However, calculating the working volume in cm³ using our online tool is much simpler and faster. This is particularly useful if you need the calculations to estimate engine power, as these indicators are directly related.
Calculating ICE volume with the calculator
To calculate the volume of the engine in question, you need to enter 3 figures into the corresponding fields — the result will appear automatically. All three values can be found in the car's owner's manual or technical specifications. Alternatively, a vernier caliper can help determine the piston dimensions.
Thus, if you get a result of 1598 cm³, in litres it will be designated as 1.6 L, and if the number is 2429 cm³, it is 2.4 litres.
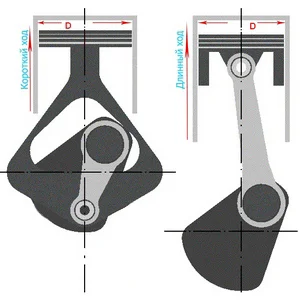
Long-stroke and short-stroke piston
Also, note that engines with the same number of cylinders and displacement can have different cylinder diameters and piston strokes. Consequently, the power characteristics of such motors will differ. An engine with short-stroke pistons (oversquare) consumes more fuel and may have lower thermal efficiency but achieves high power at high RPM. Long-stroke engines (undersquare) are used where torque and fuel economy are required.
Therefore, to the question "how to find engine displacement by horsepower", the firm answer is — you can't. Although horsepower is related to engine size, you cannot calculate the volume from it, as the formula for their relationship includes many other variables. You can only determine the engine's cubic centimetres accurately by using the piston parameters.
Why verify engine displacement?
Most often, people calculate engine displacement when they want to increase the compression ratio, typically by boring out the cylinders for tuning purposes. The higher the compression ratio, the greater the pressure on the piston during mixture combustion, and consequently, the more powerful the engine. The technique of increasing displacement to boost the compression ratio is very effective — the portion of the fuel mixture remains the same, but the useful work increases. However, there is a limit; excessive increase risks self-ignition, leading to detonation (knocking or pinking), which not only reduces power but threatens to destroy the engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is engine displacement measured in?
Engine displacement is measured in cubic centimetres (cm³ or cc), but in documentation, it is often written in litres (L). 1000 cubic centimetres equal 1 litre. The most precise unit of measurement is cubic centimetres because when car engine displacement is stated in litres, it is rounded to one decimal place. For example, a 2.4 L engine might actually be 2429 cm³.
-
What is the formula for engine cylinder working volume?
The working volume of an engine cylinder equals the product of Pi (3.1415), the square of the base radius, and the piston stroke height. The formula for ICE cylinder volume in cubic centimetres looks like this: V_work = π⋅r²⋅h/1000. Or using the alternative formula: V=(πD²/4)h.
-
How do I measure car engine displacement?
Engine displacement is the sum of the working volumes of all its cylinders. Accordingly, you must first find the volume of one cylinder and then multiply by the number of cylinders. Cylinder volume is calculated by multiplying the height by the square of the radius and Pi. To measure the exact working volume, take the piston stroke length from BDC to TDC as the height. The radius can be measured with a ruler or caliper by first finding the cylinder diameter (bore). This method is possible only with the cylinder head removed or if the specifications are already known.
-
1.8 L engine volume in cm³
Strictly speaking, 1.8 litres equals 1800 cm³. However, regarding engine displacement, this value varies because manufacturers round the precise cm³ measurement to get the 1.8 figure. It could be 1799, 1761, or even 1834 cm³. Therefore, the exact displacement of a "1.8" engine in cm³ can only be found in the technical specifications of the specific vehicle.
Was this tool useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials






Discussion (0)
No comments yet!