Error P0420: Symptoms, causes and fixing low catalyst efficiency

P0420 — error code "low catalyst efficiency"
The error code P0420 stands for: "Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold". This indicates very poor throughput or chemical efficiency of the catalytic converter. If the vehicle is equipped with two converters, this error may also appear as code P0430. In English, the fault description is Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) or (Bank 2). It is not difficult to guess that the problem most likely indicates the end of the catalytic converter's service life, although there is hope that it is simply bad fuel or the second lambda sensor has failed.
Conditions for DTC P0420 formation
During monitoring, the ECM compares the signals of the 1st and 2nd sensors over a specified time interval, calculating the duration of the voltage signal. If it exceeds the specified threshold, the car's ECU interprets this as a malfunction of the converter. The threshold value for the difference between the amplitudes of the front S1 (taken as a reference) and rear S2 oxygen sensors is more than 0.7 times per minute. However, the check engine light, signalling that the error has been recorded in the ECM memory, does not light up immediately, but only when the reduction in catalytic converter efficiency characteristics occurs for 100 seconds, with the engine load being between 21 and 63% at a crankshaft rotation of 1,720 — 2,800 rpm, and the catalyst temperature exceeding 500 degrees Celsius.
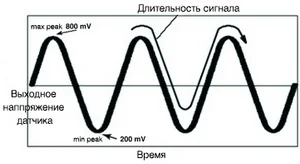
Signal from the oxygen sensor
When the catalytic converter is functioning normally, the signal from the heated oxygen sensor located at the outlet switches slowly between rich and lean states. Frequent switching of the lambda probe between these states indicates a decrease in converter efficiency. As a result, its ability to store oxygen is reduced.
The task of the catalyst is to oxidise carbon monoxide and neutralise hydrocarbon CO2 emissions in order to reduce the concentration of harmful substances. Starting with the Euro-3 standard, this process is monitored by two oxygen sensors. There is a constant comparison of the signals from the first and second lambda probes to register the convergence of their readings. Therefore, error code P0420 will eventually affect all car owners, including makes such as: Nissan, Toyota, Chevrolet, Ford, Honda or others produced after 1996 that have 2 lambda probes in the exhaust system.
Fault code P0420 appears when oxygen and residues of unburnt fuel are detected in the exhaust gases.
How the car behaves (symptoms of error P0420)
Depending on which of the two catalyst failure scenarios occurs (clogged or breaking apart), the car will exhibit specific symptoms. Apart from the Check Engine light illuminating on the dashboard (and in some cars, a catalyst overheat light), the exhaust gases will no longer comply with Euro 3-5 standards. In general, the signs that accompany error P0420 (P0430) can be:
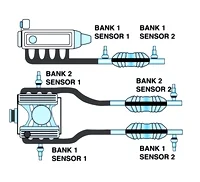
Location of the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors
- increased fuel consumption;
- reduced engine performance;
- change in the smell of exhaust gases (becoming very unpleasant, often like rotten eggs);
- rattling from the catalytic converter area (if the internal honeycomb is crumbling);
- sometimes unstable idle;
- difficulty starting the engine may occur. So, if you observe more than two of these signs simultaneously, the car likely has problems with the catalytic converter, and diagnostics are essential to confirm the fault code!
Main causes of code P0420
With proper use, the service life of a catalytic converter is at least 200,000–250,000 km. However, if you regularly use fuel containing impurities with a high concentration of lead, its destruction will be accelerated. Also, due to poor fuel or faulty ignition and valve timing, compression is compromised and misfires appear, which directly contributes to both the reduction of the catalytic converter's life and the appearance of error code P0420 or P0430.
So, the main possible causes are:
- Use of leaded petrol.
- Damaged or failed oxygen sensor S2.
- Short circuit in the "downstream" oxygen sensor circuit.
- Damage to the catalytic converter itself.
- Damage to the exhaust system (exhaust manifold, silencer, pipes, gaskets, etc.).
- Prolonged operation of the car with misfires in the cylinders.
- High fuel pressure in the system.
As you can see, there can be at least 7 reasons why error P0420 pops up, although often it is much simpler, and drivers face the need to remove or replace the catalyst and install a sensor emulator. For the luckiest ones, when this fault appears at a lower mileage, it is enough to fill up with high-quality petrol or check the lambda sensor contacts.

3 main reasons why error P0420 appears and how to fix it.
To correctly identify the malfunction that caused this code, it is necessary to perform a thorough diagnosis of all possible causes.
Check methods and solving the problem
In some cases, it is necessary to check the oxygen sensor for faults or the exhaust system and manifold for leaks. Leaks and air intake can affect O2 sensor operation and cause error code P0420, but most often, this problem is directly related only to the condition of the catalytic converter.
A few tips on the elimination plan
Before starting diagnostics, to save time on finding the cause and fixing the problem, we advise performing a few simple checks before proceeding to more complex solutions. So:
- First of all, remember which petrol station you used and whether you filled up with the same fuel as usual. Also, ensure that symptoms of coolant entering the engine, as well as oil consumption, are absent.
- Check the ignition timing. Retarding the ignition timing below the required level can increase exhaust gas temperature and, over time, reduce catalyst efficiency.
- Check the connector of the 2nd ("rear") oxygen sensor. Having ensured that all this is unchanged, you will have to connect a computer to retrieve data from the electronic control unit.
Checking the operation of the catalytic converter and its parameters
To assess the efficiency of the catalyst, it is necessary to compare the output voltage graphs between the "upstream" and "downstream" oxygen sensors, as well as look at the fuel trim data.
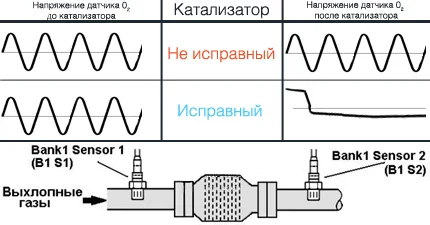
Oxygen sensor readings on an oscilloscope
The output voltage of the oxygen sensor, read by the car's computer, will decrease when the mixture is lean and increase when it is rich. Normal reading for the oxygen sensor will fluctuate between 900 millivolts (rich state) and 100 millivolts (lean state).
Short-term fuel trim should ideally aim for "0", but on an engine with mileage, deviations from the norm up to 10% are acceptable. However, when the fuel trim exceeds 25%, long-term trim also arises, so if both values are present, this indicates a problem with the preparation of the air-fuel mixture. Therefore, pay attention to the presence of additional fault codes.
How to rectify the fault associated with error P0420
Some car owners, not knowing the origin of error P0420, may start fixing the problem by cleaning the throttle body or replacing sensors affecting air and fuel flow. Whereas, if anything needs to be replaced, it is:
Firstly – swap the lambda probes, upstream and downstream, since they are often identical and can substitute each other. Consequently, if the problem is specifically in a faulty second oxygen sensor, the error code will change (alternatively, error P0134 may appear).
Secondly – fill up with different petrol, of higher quality, and drive for a while (if it is due to fuel, a couple of days will change the situation).
The third step towards eliminating the malfunction can be checking the catalytic converter, or more precisely, its throughput (there are several methods). Internal destruction of the catalyst usually occurs due to abnormal operation of engine systems upstream of the catalyst. Increased operating temperature of the converter is usually the cause of both the appearance of this code and its failure. For example, misfires can lead to an elevated catalyst operating temperature.
How to solve the problem of low catalyst efficiency
Since error P0420 most often pops up when the catalytic converter has served its time, most likely, the problem of low catalyst system efficiency below the threshold will have to be solved by replacing it with a working one or remapping the ECM to a different toxicity standard (e.g., EURO2).

The most expensive repair method is replacing the catalyst with a new original one.
Significantly cheaper is to replace it with a universal catalytic converter. Its efficiency is somewhat worse (the original is usually ceramic, while this is often metal), and the service life is shorter, and not all cars will react positively to such a change. However, you will not have to make any software changes.
If emissions standards are not critical to you, a relatively inexpensive option is the installation of a flame arrester. This solution involves cutting out the catalyst canister and installing a cheat device (emulator) for the second lambda.
A budget option, involving remapping and installing a cheat device (mechanical or electronic), is converting the car to a lower toxicity standard. Such a solution to problems appearing with code P0420 will not only eliminate the malfunction but also allow the engine to "breathe freely", as all these norms significantly curtail power capabilities for the sake of compliance with environmental standards. This method involves removing the catalyst from the exhaust system, and installing a two-channel emulator will allow precise tuning of response time parameters, signal speed and its offset.
And if the throughput of the catalytic converter is still within normal limits (0.21 kg/cm² at 2000 rpm), since the signal about the need to replace the catalyst can appear even at 70% efficiency, you can temporarily install a spacer under the lambda probe. This solution is the cheapest, but it is not a panacea and is not suitable for everyone.
I hope the methods described above for solving the malfunction associated with code P0420 help you, and you will no longer have questions like: "why did error P0420 appear and how to fix it", and you will share the knowledge gained on social networks with friends. Please write us a review on whether you managed to fix the problem and exactly which method helped to sort out the cause of the weak catalyst efficiency.
Additional materials on the topic:
- How to check a catalytic converter?
- DIY catalyst repair
Was this article useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials







Discussion (0)
No comments yet!