Tyre Load Index Calculator
The tyre load rating (or more commonly, the load index) can be approximately calculated based on information from the vehicle handbook and the characteristics provided by the car manufacturer. Tyre load calculations are performed by dividing the maximum permissible mass of the vehicle by 4 (the number of wheels on standard passenger cars and SUVs).
Before calculating the tyre load index, it is necessary to define the terms found in the vehicle's technical passport. These are:
- Dry weight — the weight of the car without passengers, spare wheel, tools, or repair kits, and without technical fluids (fuel, oils, cleaning fluids, etc.);
- Kerb weight — the weight of the vehicle with technical fluids (fuel, oils, etc.) and the driver (sometimes called mass in running order);
- Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) — the maximum weight of the fully equipped and loaded vehicle (with passengers, fluids, tool kit, and payload; also known as Maximum Authorised Mass);
- Payload capacity — the weight of the useful load the vehicle can carry (passengers, luggage).
As a rule, the permissible payload is not written in the registration document but is indicated in the manufacturer's technical documentation. In accordance with European standards, the average weight of a person sitting in a car is assumed to be 75 kg.
Remember that the Maximum Authorised Mass (Gross Vehicle Weight) is the sum of the vehicle's unladen weight (kerb weight) and its payload capacity. Therefore, it is easiest to calculate the tyre load index if you know the vehicle's Gross Vehicle Weight. To do this, simply divide its value by 4. The result is the number of kilograms a tyre can support. You should add 35–40% to this value as a safety margin. Then, use the table to determine which tyre load index corresponds to this value.
If the maximum permissible mass of the car is unknown to you, you can perform an empirical calculation based on theoretical data. That is, add the kerb weight of the car and its payload capacity. Then divide the resulting value by 4 to select tyres by load index. In the calculator above, we have included a 40% margin so that you can select a tyre not at its limit, but with a certain reserve of strength. This is especially relevant for roads with poor surfacing.
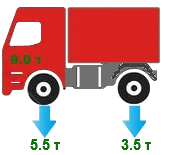
Do not forget that on many cars, the load on the front and rear axles differs. Therefore, use our empirical calculation carefully, and whenever possible, refer to reference information and the manufacturer's recommendations on which load index tyres to use.
It is worth remembering that you must choose tyres recommended by the manufacturer, or close to these requirements. If you choose tyres with a lower rating, you risk your own safety while driving. The tyre will be subjected to excessive loads. This means that at some point, it could simply blow out. If this happens at speed, the consequences can be unpredictable.
However, you should not fit tyres that are too stiff either. If you do so, you will encounter three negative factors:
- Increased fuel consumption. This is because the engine needs more energy to rotate a heavier and stiffer tyre.
- Ride stiffness. As the load index increases, the rubber becomes stiffer. Consequently, the car's ride will also be harsh and uncomfortable.
- Excessive load on the suspension. Stiffer tyres also have greater mass. Consequently, additional force is exerted on the suspension, leading to excessive wear and shortening its service life.
Therefore, stick to the "golden mean" and install tyres with the load index recommended by the manufacturer.
How to use the calculator
Follow this algorithm:
- In the "Kerb weight value" field, enter the vehicle weight with a full tank, technical fluids, repair kit, spare wheel, and driver. Usually, this value is indicated in the vehicle handbook or manufacturer's documentation.
- In the "Maximum permissible luggage weight" field, enter the weight of the cargo you intend to carry in the car. Note that you do not need to account for the weight of passengers, as it is already included (calculated as 4 passengers weighing 75 kg each). This information can also be found in your car's reference documentation or online.
- Click the "Calculate" button. In the result field, you will see the load index value for your vehicle's tyres.
We repeat that the calculations are empirical, and therefore we recommend verifying the coefficient values in reference literature.
| Tyre Load Index and Maximum Vehicle Weight Table | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Index | Max Weight, kg | Load Index | Max Weight, kg |
| 80 | 450 | 102 | 850 |
| 81 | 462 | 103 | 875 |
| 82 | 475 | 104 | 900 |
| 83 | 487 | 105 | 925 |
| 84 | 500 | 106 | 950 |
| 85 | 515 | 107 | 975 |
| 86 | 530 | 108 | 1000 |
| 87 | 545 | 109 | 1030 |
| 88 | 560 | 110 | 1060 |
| 89 | 580 | 111 | 1090 |
| 90 | 600 | 112 | 1120 |
| 91 | 615 | 113 | 1150 |
| 92 | 630 | 114 | 1180 |
| 93 | 650 | 115 | 1215 |
| 94 | 670 | 116 | 1250 |
| 95 | 690 | 117 | 1285 |
| 96 | 710 | 118 | 1320 |
| 97 | 730 | 119 | 1360 |
| 98 | 750 | 120 | 1400 |
| 99 | 775 | 121 | 1450 |
| 100 | 800 | 122 | 1500 |
| 101 | 825 | 123 | 1550 |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the tyre load index for passenger cars?
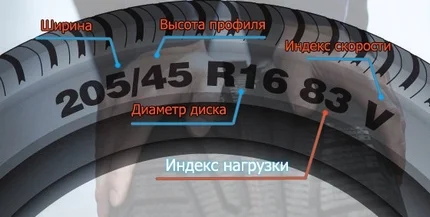
The tyre load index for passenger cars is expressed as a two-digit number. For passenger car tyres, coefficients range from 63 to 90. Remember that the higher the load index, the thicker, stiffer, and heavier the tyre. Consequently, there will be more noise when driving, and fuel consumption will increase. Conversely, the lower the index, the softer and lighter the rubber, though it will wear out faster.
-
What is the tyre load index for SUVs/Crossovers?
The load index for SUV and crossover tyres is usually expressed as a three-digit number, which immediately follows the rim diameter in the markings. Tyres for crossovers also often have an increased load capacity index and are necessarily accompanied by an additional designation – XL (Extra Load or Reinforced). This indicates that the rubber has a higher strength rating and that the tyre sidewall is much stronger than usual. Most often, the load index for crossover tyres falls within the range of 90 to 105.
-
What is load index 91?
Load index 91 is a number indicating that the tyre is capable of carrying a load of 615 kg at the maximum speed indicated in the tyre markings (the speed index is marked with a Latin letter immediately after the load designation). On the tyre sidewall, this might look like this, for example: 205/55 R16 91 H.
-
What does load index 65 mean?
Index 65 means that the tyre can withstand a load of 290 kg. This means that in total, a car with wheels fitted with such rubber can carry a weight, including payload, of no more than 290 × 4, i.e., 1160 kg. This assumes the tyre is inflated to nominal internal pressure and the speed does not exceed the permissible limit (indicated by the manufacturer with a letter index).
Was this tool useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.






Discussion (0)
No comments yet!