Engine Oil Markings
Every car owner should know how to decode the engine oil markings printed on the product packaging. The key to a durable and stable engine is the use of high-quality motor oil with specifications that meet all the manufacturer's requirements. These strict requirements exist because oils must operate across a wide temperature range and under high pressure.

Engine oil markings contain all the necessary information for making the right choice; you just need to know how to decode them.
To organise and simplify the procedure of selecting oil for a specific engine type based on required characteristics and tasks, a number of international standards have been developed. Global oil manufacturers use these generally accepted classifications:
- SAE;
- API;
- ACEA;
- ILSAC;
- GOST (National Standards).
Each type of oil marking has its own history and market share, and decoding its meaning allows you to navigate the choice of the necessary lubricant. The most commonly used classifications are API and ACEA.
There are two main classes of motor oils, depending on the engine type: petrol or diesel, although universal oils also exist. Usage data is always indicated on the label. Any engine oil consists of a base composition (mineral oil) and specific additives. The lubricant base consists of oil fractions obtained from refining crude oil or created artificially. Therefore, by chemical composition, they are divided into:
- mineral;
- semi-synthetic;
- synthetic.
The chemical composition is always indicated on the canister alongside other markings.
What you might find on an oil container label:
- SAE viscosity grade.
- API and ACEA specifications.
- Car manufacturer approvals.
- Barcode.
- Batch number and production date.
- Pseudo-markings (not generally accepted standard markings, but used as a marketing ploy, e.g., 'fully synthetic', 'HC', 'with intelligent molecules', etc.).
- Special motor oil categories.
To help you buy exactly the oil that suits your car's engine best, we will decode the most important engine oil markings.
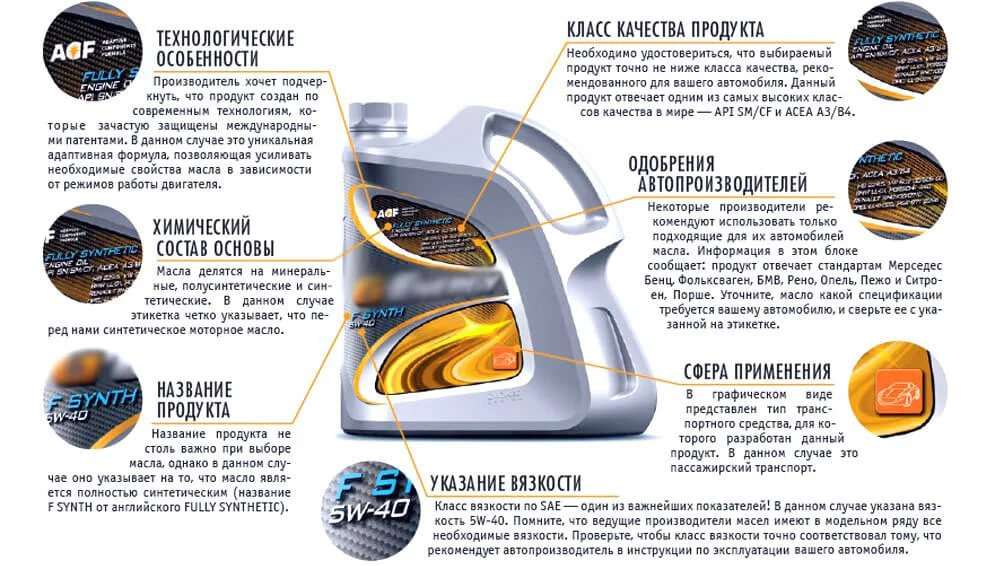
SAE Engine Oil Markings
The most important characteristic indicated on the canister is the viscosity coefficient according to the SAE classification. This is an international standard regulating oil viscosity at positive and negative temperatures (limit values).
According to the SAE standard, oils are designated in the format XW-Y, where X and Y are numbers. The first number is a code for the minimum temperature at which the oil pumps normally through the channels and the engine turns over without difficulty. The letter 'W' stands for Winter.
| Values | 0W | 5W | 10W | 15W | 20W | 25W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cranking | -30°С | -25°С | -20°С | -15°С | -10°С | -5°С |
| Pumping | -40°С | -35°С | -30°С | -25°С | -20°С | -15°С |
The second number conditionally signifies the minimum and maximum limit of the oil's high-temperature viscosity when heated to operating temperature (+100…+150°С). The higher the number, the thicker the oil is when heated, and vice versa.
| 5W — 30 | from minus 25 to plus 20 |
| 5W — 40 | from minus 25 to plus 35 |
| 10W — 30 | from minus 20 to plus 30 |
| 10W — 40 | from minus 20 to plus 35 |
| 15W — 30 | from minus 15 to plus 35 |
| 15W — 40 | from minus 15 to plus 45 |
| 20W — 40 | from minus 10 to plus 45 |
| 20W — 50 | from minus 10 to plus 45 and above |
| SAE 30 | from 0 to plus 45 |
Therefore, oils are necessarily divided into three types depending on viscosity:
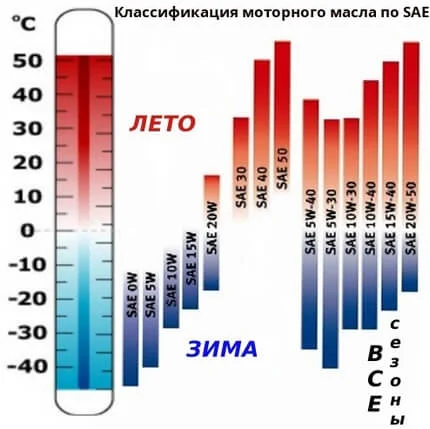
- Winter oils: these are more fluid and ensure trouble-free engine starting in the cold season. The SAE indicator for such oil will contain the letter 'W' (e.g., 0W, 5W, 10W, 15W, etc.). To understand the limit value, subtract 35. In hot weather, such oil cannot provide a lubricating film or maintain the necessary pressure in the oil system because its fluidity becomes excessive at high temperatures;
- Summer oils: used when the average daily temperature is not below 0°C, as their kinematic viscosity is high enough so that fluidity does not exceed the required value for good engine part lubrication in hot weather. Starting an engine with such high viscosity is impossible at freezing temperatures. Summer oil grades are designated by a numerical value without letters (e.g., 20, 30, 40, and so on; the higher the number, the higher the viscosity). The density of the composition is measured in centistokes at 100 degrees (e.g., a value of 20 indicates a limit density of 8-9 centistokes at an engine temperature of 100°C);
- Multigrade (All-season) oils: the most popular as they can operate at both negative and positive temperatures, the limit values of which are indicated in the SAE decoding. Such oil has a double designation (example: SAE 15W-40).
Viscosity characteristics are the first and most important element of engine oil classification and marking, but not the only one — choosing oil strictly by viscosity is incorrect. It is always necessary to choose the correct balance of properties for the oil and its operating conditions.
Besides viscosity, every oil has a different set of performance properties (detergent, anti-oxidation properties, anti-wear, tendency to form deposits, corrosiveness, etc.). These allow determining their possible area of application.
API Engine Oil Markings
In the API classification, the main indicators are: engine type, engine operating mode, oil performance properties, application conditions, and year of manufacture. The standard provides for the division of oils into two categories:
- Category 'S' – indicates oils designed for petrol engines;
- Category 'C' – indicates oils designed for diesel vehicles.
How to decode API markings?
As we have established, the API designation can start with the letter S or C, indicating the engine type suitable for the oil, followed by another letter indicating the oil class, showing the level of performance properties.
According to this classification, decoding engine oil markings is done as follows:
- the abbreviation EC, found immediately after API, denotes Energy Conserving oils;
- Roman numerals after this abbreviation indicate the level of fuel economy;
- the letter S (Service) denotes the use of oil for petrol engines;
- the letter C (Commercial) denotes oils for diesel motors;
- one of these letters is followed by the level of performance properties, indicated by letters from A (the lowest level) to N and beyond (the further the second letter is in the alphabet, the higher the oil class);
- universal oil has letters from both categories separated by a slash (e.g., API SL/CF);
- API marking for diesel is divided into two-stroke (number 2 at the end) and four-stroke (number 4).
Currently, category 'S' consists of 13 classes of motor oils, some of which are obsolete, so we will list only the most relevant ones:
| Year of introduction | 1980 | 1989 | 1994 | 1997 | 2001 | 2004 | 2010 | 2020 |
| API oils for petrol engines | SF | SG | SH | SJ | SL | SM | SN | SP |
Category 'C' currently consists of 14 classes, half of which are also no longer used. You may encounter the following markings:
| Year of introduction | 1983 | 1990 | 1994 | 1998 | 2004 | 2010 |
| API oils for diesel engines | CE | CF-4 | CF, CF-2, CG-4 | CH-4 | CI-4 | CJ-4 |
Those motor oils that have passed API/SAE testing and meet the requirements of current quality categories are marked on labels with a round graphic symbol (the 'Donut'). The top part says 'API' (API Service), the centre shows the SAE viscosity grade, and the bottom may show the degree of energy conservation.
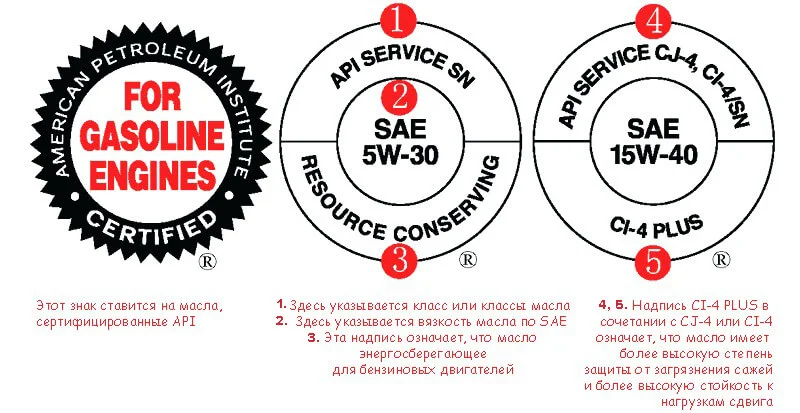
Using oil according to its specific specification reduces wear and the risk of engine failure, decreases oil consumption ('burn-off') and fuel consumption, reduces noise, improves engine running characteristics (especially at low temperatures), and increases the service life of the catalytic converter and exhaust treatment system.
ACEA, GOST, ILSAC Classifications and How to Decode Them
ACEA Motor Oil Classification
The ACEA classification was developed by the Association of European Automobile Manufacturers. It specifies performance properties, applications, and motor oil categories. ACEA classes are also divided into diesel and petrol.
The latest edition of the standard provides for the division of oils into 3 categories and 12 classes:
- A/B – petrol and diesel engines of passenger cars, vans, and minibuses (A1/B1-12, A3/B3-12, A3/B4-12, A5/B5-12);
- C – petrol and diesel engines with exhaust gas catalytic converters (C1-12, C2-12, C3-12, C4-12);
- E – diesel engines of heavy-duty trucks (E4-12, E6-12, E7-12, E9-12).
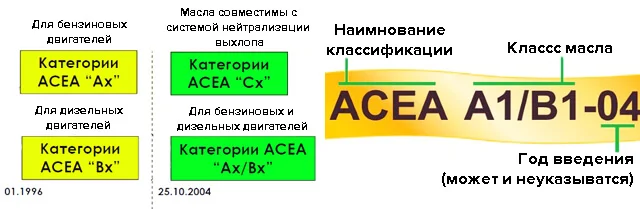
In the ACEA designation, in addition to the motor oil class, the year of its introduction is indicated, as well as the edition number (when technical requirements were updated).
GOST Motor Oil Classification (Russia)
According to the Russian standard GOST 17479.1-85, motor oils are divided into:
- classes by kinematic viscosity;
- groups by performance properties.
By kinematic viscosity, oils are divided into the following classes:
- summer – 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 20, 24;
- winter – 3, 4, 5, 6;
- all-season – 3/8, 4/6, 4/8, 4/10, 5/10, 5/12, 5/14, 6/10, 6/14, 6/16 (the first number indicates the winter class, the second the summer class).
In all listed classes, the higher the numerical value, the greater the viscosity.
By area of application, all motor oils are divided into 6 groups – designated from the letter 'A' to 'E'.
Index '1' designates oils intended for petrol engines, index '2' for diesel engines, and oils without an index indicate universality.
ILSAC Motor Oil Classification
ILSAC is a joint invention of Japan and America; the International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee has issued 6 motor oil standards: ILSAC GF-1, GF-2, GF-3, GF-4, GF-5, and GF-6. They are completely analogous to API classes, the only difference being that oils meeting ILSAC classification are energy-conserving and all-season. This classification is best suited for Japanese cars.
Correspondence of ILSAC categories relative to API:
- GF-1 (obsolete) — quality requirements are analogous to API SH category; viscosity SAE 0W-XX, 5W-XX, 10W-XX, where XX is 30, 40, 50, 60.
- GF-2 — corresponds to API SJ quality requirements, and viscosity SAE 0W-20, 5W-20.
- GF-3 — is an analogue of API SL category, introduced in 2001.
- ILSAC GF-4 and GF-5 — respectively analogues of SM and SN.
- ILSAC GF-6 — corresponds to the new SP standardization.
Additionally, within the ILSAC standard for Japanese cars with turbocharged diesel engines, the JASO DX-1 class is used separately. This automotive oil marking caters for engines of modern cars with high environmental parameters and built-in turbines.
Certification and Manufacturer Approvals
The API and ACEA classifications formulate minimal basic requirements agreed upon between oil and additive manufacturers and car manufacturers. Since engine designs of different brands differ, oil operating conditions in them are not exactly the same. Some major engine manufacturers have developed their own motor oil classification systems, so-called approvals, which complement the ACEA classification system, utilizing their own test engines and field trials. Engine manufacturers such as VW, Mercedes-Benz, Ford, Renault, BMW, GM, Porsche, and Fiat predominantly use their own approvals when selecting oil for the engine. The car's owner manual always contains specifications, and their numbers are printed on the oil packaging next to the designation of its performance class.
Let's look at and decode the most popular and frequently used approvals found on motor oil canisters.
VAG Group Approvals for Passenger Cars
VW 500.00 — energy-conserving motor oil (SAE 5W-30, 10W-30, 5W-40, 10W-40, etc.), VW 501.01 — all-season, intended for use in conventional petrol engines produced before 2000, and VW 502.00 for turbocharged ones.
The VW 503.00 approval stipulates that this oil is for petrol engines with SAE 0W-30 viscosity and an extended drain interval (up to 30,000 km), and if the exhaust system has a three-way catalytic converter, then oil with the VW 504.00 approval is filled into the engine of such a car.
For Volkswagen, Audi, and Skoda cars with diesel engines, a group of oils with VW 505.00 approvals for TDI motors produced before 2000 is provided; VW 505.01 is recommended for PDE engines with Unit Injectors (Pumpe-Düse).
Energy-conserving motor oil with viscosity class 0W-30 and VW 506.00 approval has an extended replacement interval (for V6 TDI motors up to 30,000 km, 4-cylinder TDI up to 50,000 km). Recommended for new generation diesel engines (manufactured after 2002). For turbocharged motors and Unit Injector PD-TDI, it is recommended to fill with oil having the VW 506.01 approval, which has the same extended drain interval.
Mercedes Passenger Car Approvals
The Mercedes-Benz group also has its own approvals. For example, motor oil with the designation MB 229.1 is intended for diesel and petrol Mercedes engines manufactured since 1997. Approval MB 229.31 was introduced later and corresponds to SAE 0W-, SAE 5W- specifications with additional requirements limiting sulfur and phosphorus content. MB 229.5 is an energy-conserving oil with an extended service life for both diesel and petrol motors.

Certification and Manufacturer Approvals
BMW Motor Oil Approvals
BMW Longlife-98: oils with this approval are intended for engines in cars manufactured since 1998. An extended service replacement interval is provided. Corresponds to basic ACEA A3/B3 requirements. For engines produced at the end of 2001, the use of oil with the BMW Longlife-01 approval is recommended. The BMW Longlife-01 FE specification provides for the use of car oil when operating in severe conditions. BMW Longlife-04 is approved for use in modern BMW motors.
Renault Motor Oil Approvals
The Renault RN0700 approval was introduced in 2007 and corresponds to basic requirements: ACEA A3/B4 or ACEA A5/B5. Renault RN0710 meets ACEA A3/B4 requirements, and Renault RN 0720 meets ACEA C3 plus additional Renault requirements. Approval RN0720 was developed for use in the latest generation diesel engines with Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF).
Ford Car Approvals
SAE 5W-30 motor oil with Ford WSS-M2C913-A approval is intended for initial and service changes. This oil meets ILSAC GF-2, ACEA A1-98, and B1-98 classifications and additional Ford requirements.
Oil with Ford M2C913-B approval is intended for initial filling or service replacement in petrol and diesel engines. It also meets all ILSAC GF-2 and GF-3, ACEA A1-98, and B1-98 requirements.
The Ford WSS-M2C913-D approval was introduced in 2012; oils with this approval are recommended for all Ford diesel engines except for Ford Ka TDCi models produced before 2009 and engines produced between 2000 and 2006. It provides for the possibility of an extended drain interval and fuelling with bio-diesel or high-sulphur fuel.
Oil with the Ford WSS-M2C934-A approval provides for an extended replacement interval and is intended for cars with a diesel engine and a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF). Oil corresponding to the Ford WSS-M2C948-B specification is based on the ACEA C2 class (for petrol and diesel engines with a catalytic converter). This approval requires oil with a viscosity of 5W-20 and reduced soot formation.
When choosing oil, you need to remember a few main points: the correct choice of the necessary chemical composition (mineral, synthetic, semi-synthetic), the viscosity classification parameter, and knowledge of the necessary requirements regarding the additive package (defined in API and ACEA classifications). The label must also contain information on which car brands the product is suitable for. It is equally important to pay attention to additional motor oil designations. For example, the Long Life marking indicates that the oil is suitable for cars with an extended service replacement interval. Also among the features of some compositions, one can highlight compatibility with engines having turbocharging, intercoolers, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) cooling, variable valve timing, and valve lift control.
Was this article useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our content.
Related Materials





Discussion (0)
No comments yet!